Crypto is estimated to grow to 2 Billion by the end of 2023, and it is crucial to understand how blockchain can scale while still maintaining its decentralized and secure nature. There are a few different ways to scale blockchain, such as increasing the size of blocks, implementing a lightning network, or a combination of both. Increasing the size of blocks will enable more transactions to be processed in a single block, while the lightning network allows for faster, off-chain transactions. It is also important to consider the security implications of scaling blockchain. As the network grows, it becomes more challenging to ensure that all the nodes are secure and that the data is properly protected. To ensure that these security measures are in place, it is important to have proper protocols and security protocols that are regularly updated and tested. With the right scaling strategies, blockchain can continue to grow while still maintaining its decentralized and secure nature.
What is blockchain scalability?
Blockchain scalability is an important factor for the success of any blockchain platform. It refers to the ability of the platform to support a growing number of transactions and an increasing number of nodes in the network. The scalability of the blockchain increases its usability and efficiency, allowing it to handle more transactions and users. To increase scalability, blockchain networks can employ different solutions such as sharding, sidechains, and other advanced technologies. With these solutions, blockchain networks can process more transactions faster and with less energy consumption. All in all, blockchain scalability is an important factor for the successful deployment of blockchain technology.
Why is scaling important?
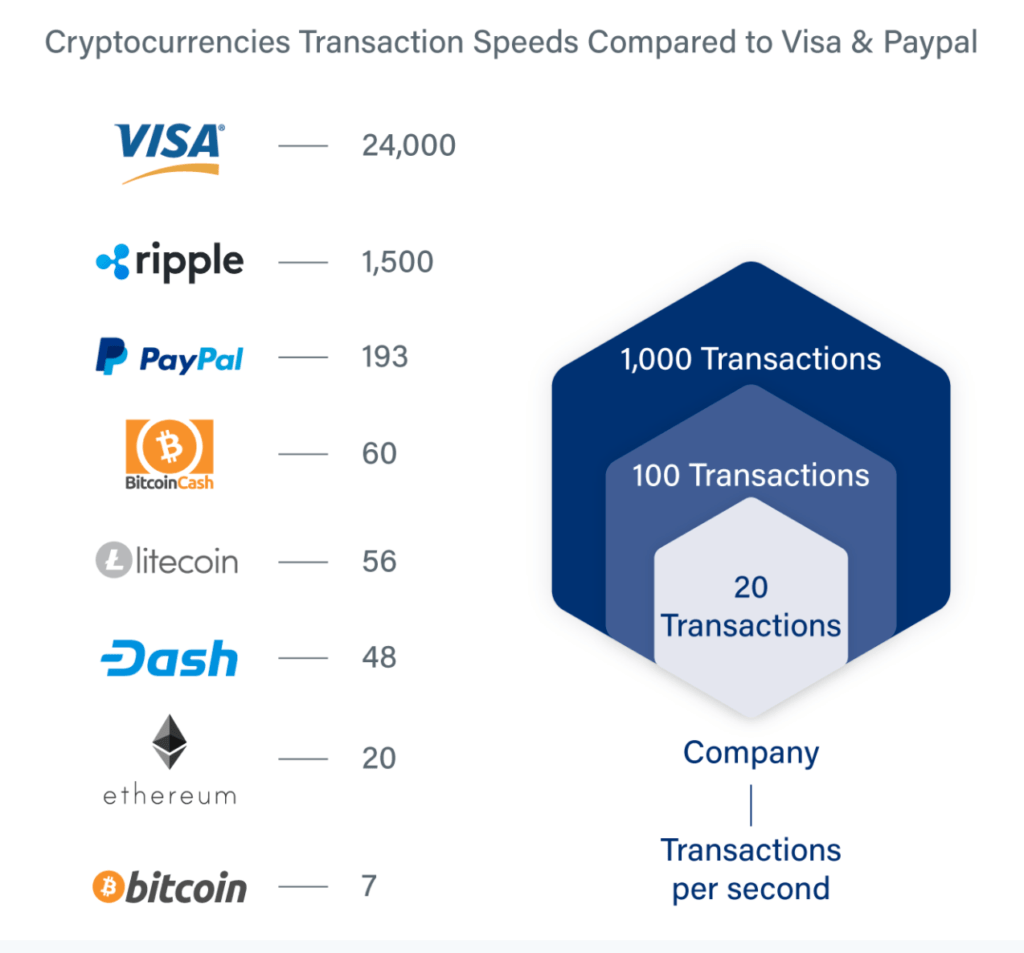
Scaling is incredibly important for blockchain networks as the number of users continues to grow exponentially. Just in the last year, the number of users on cryptocurrency platforms has grown from 101 million in January 2021 to 295 million in December 2021. This rapid growth means that the blockchain networks need to scale up in order to keep up with the demand and provide the same kind of transaction speeds as centralized platforms. Without scaling, blockchain networks would be unable to keep up with the number of users and would be unable to compete.
Increasing block time or size to increase scaling would reduce security and decentralization.
Increasing block time or size is a proposed solution to the scaling issue of blockchain networks, but this would come with a major risk to the security and decentralization of the network. With larger blocks, more data has to be processed, and this would require more powerful nodes, which would lead to less decentralization as larger entities would be able to run more powerful nodes. Furthermore, larger blocks would also increase the risk of a successful double spending attack as more transactions could be included in the malicious block. Therefore, increasing block time or size to increase scaling would ultimately reduce security and decentralization.
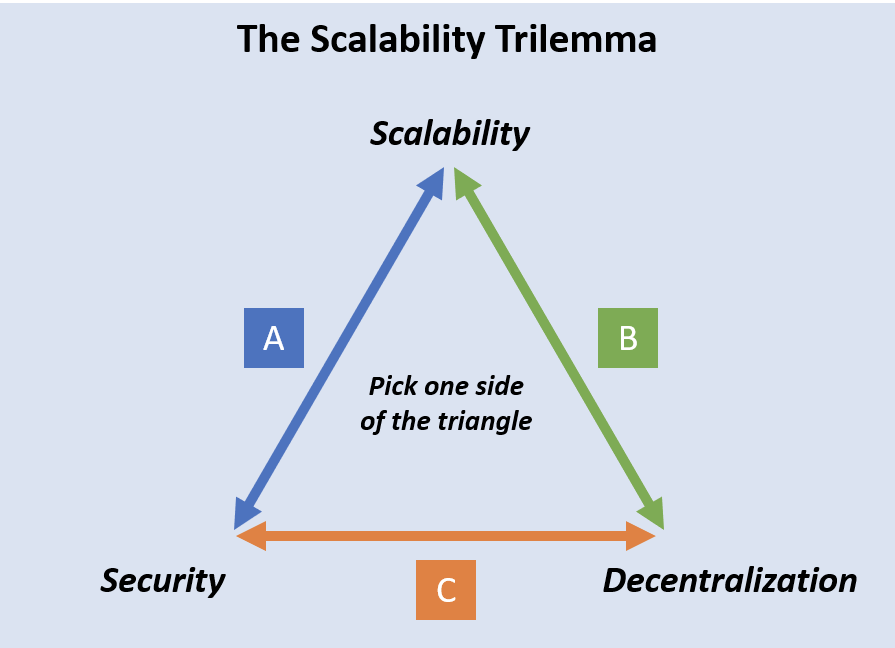
What is the blockchain trilemma?
The blockchain trilemma is a concept that suggests that it is impossible to have a blockchain that is simultaneously secure, decentralized, and scalable. This concept was first introduced by Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin, who stated that a blockchain can only have two out of the three mentioned properties at any given time. This means that if developers want to make a blockchain more secure, they must sacrifice either decentralization or scalability. Similarly, if they want to make a blockchain more scalable, they must sacrifice either security or decentralization. As such, developers must choose which two out of the three properties to focus on when creating a blockchain.
Creators can only choose 2 out of the 3 elements:
4 main issues that affect how well blockchain can scale
Scale is a major issue when it comes to blockchain technology. There are four main issues that affect how well blockchain can scale:
- transaction fees,
- hardware requirements,
- block size,
- response time.
Hardware requirements refer to the amount of computing power and storage needed to run the network; transaction fees refer to the fees associated with each transaction on the network; block size is the amount of data that can be stored in each block on the blockchain; and response time is the amount of time it takes for the blockchain to process a transaction. All four of these issues have an impact on the scalability of blockchain and must be addressed in order to ensure its success.
Transaction fees (gas) issues
The demand for higher computation power for mining has caused a ripple effect of complexity in the process of validating transactions. This means that when there is a higher demand for transactions to be verified, users will have to pay a higher fee to ensure their transactions go through. This is an unfortunate result of the increased demand for higher computation power, but one that must be taken into account when considering the cost of verifying transactions.
Hardware requirements issues
In order to maintain decentralization when processing a new transaction, the verification of blocks must be available to as many people as possible. This requires scaling with low hardware requirements so that everyone can contribute to the network and verify new blocks. Each node adds the information from the transaction to the ledger, but it is only secure when verified by a large number of users. This allows the network to remain decentralized and secure, while also making sure that the network is accessible to anyone who wishes to contribute.
Transaction fees (gas) issues
The demand for higher computation power for mining has led to more complexities in the processes for validating transactions. This means that when there is more demand, users will have to pay a higher fee in order to verify their transactions. This can be a challenge for those who rely heavily on cryptocurrency transactions, but it is necessary in order to ensure accuracy and stability when it comes to these transactions. This can be a deterrent for some users, but it is an important factor in maintaining the security of cryptocurrency networks.
Block size issues
The increasing number of transactions in blockchain networks has a direct result on the processing time for executing those transactions. The more transactions that are added to the network, the larger the block size becomes, and the more hardware requirements are needed to process them. As a result, the time it takes to process the transactions increases, making it more difficult for the network to keep up with the number of transactions being added. This has a direct impact on the speed and efficiency of the blockchain network.
Response time issues
Blockchain transactions are known for their long waiting periods for validation, as there are often many transactions ahead of any one individual transaction in the queue. This wait time can be especially long during peak times, which can be a source of frustration for users who are expecting their transaction to be processed quickly. Luckily, there are ways to reduce the wait time, such as using a faster consensus algorithm or incentivizing miners to prioritize certain transactions. Despite these options, the long wait times remain a challenge in the blockchain industry.
Address the issues in scaling
Scaling is a critical issue in the development of blockchain technology. To address scaling issues, developers have come up with four main categories of solutions. These include L1 scalability solutions, which involve modifications to the blockchain protocol itself; L2 scalability solutions, which involve off-chain transactions; scalable consensus mechanisms which are designed to allow more nodes to participate in the consensus process; and scalable distributed ledgers which provide a platform for faster transaction times. Each of these solutions has their own benefits and drawbacks, and developers are continuing to research and refine them to provide the best possible scaling solution for the blockchain.
L1 scalability solutions
L1 solutions enhance the blockchain network’s essential characteristics & attributes.
This helps increase block size limit or decrease the block verification time.
Solutions include:
- Sharding,
- Segregated Witness (SEGWIT),
- Hard Forks,
- Scalable consensus mechanisms,
- Scalable distributed ledgers
What is Sharding?
Sharding allows a blockchain network to break down into smaller, more manageable chunks known as shards.
The network would then execute the shards in parallel with one another.
The results is a quicker and more efficient transaction throughput.
What is Segregated Witness (SEGWIT)?
SEGWIT is a protocol enhancement in blockchain network focusing on changing the way & structure of data storage.
It helps eliminate signature data linked with each transaction.
The result is increased transactions capacity & storage.
What is Hard Fork?
Hard fork is a procedure that focuses on making structural or fundamental changes to a blockchain network’s properties.
While hard forking is a prerequisite for L1 blockchain scalability solutions, contentious hard fork is the most productive option.
L2 scaling solutions
Layer 2 solutions are supplementary protocols built on top of the primary blockchain.
They can be used to ‘offload’ transactions from the primary Blockchain.
- State Channels,
- Sidechains,
- Plasma,
- Lightning Network,
What are state channels?
State channels enable 2-way communication between off-chain transaction channels and blockchain networks.
It functions as resources near to the network that is integrated with the assistance of a smart contract or multi-signature method.
What are Sidechains?
Sidechains operate as transactional chains next to the Blockchain in big batch transactions.
In comparison to the primary chain, sidechains use distinct consensus techniques.
It helps solve the scalability issue in the Blockchain of your choosing.
16-3/ What is Plasma?
Plasma focuses on utilizing child chains that begin with the parent blockchain, with each child chain functioning as a separate blockchain.
Used for cases involving assuring execution of transactions in a comparable environment with enhanced security.
What is the Lightning Network?
Lightning network exploits smart contract functionality through private, off-chain channels over the main blockchain network.
Reduces the burden on the mainchain.
Users no longer have to pay mining fees for block confirmation.
Scalable Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms allows distributed systems to work together, establishing an agreed consensus of a single value or state.
Scalable consensus mechanisms include:
- Delegated Proof-of-Stake,
- Proof-of-Authority,
- Byzantine Fault Tolerance,
What is Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPOS)
DPOS is a consensus technique analogous to the democratic process of controlling a country.
It allows token holders to choose validators for network transactions (range from 10 to 100 and varies regularly).
What is Proof-of-Authority (POA)
POA is a scalable consensus method with a reputation-based consensus algorithm.
The chosen nodes are in charge of validating network transactions using the Proof-of-Authority consensus technique.
What is Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)
BFT consensus techniques have been one of the most reliable tools for dealing with the Byzantine Generals Problem.
It suggests the necessity for continual consensus, despite multiple antagonistic participants in the network.
Scalable distributed ledgers
Blockchain technology is only part of the larger distributed ledger technology (DLT) environment.
Other forms of distributed ledgers that do not organize transactions into chained, sequential blocks may also be the path to scalability.
What is Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG)
DAG is one such example of alternative distributed ledger technology that does not use the data structure of traditional blockchains.
Transactions run asynchronously, & theoretically allow an infinite number of transaction processing.
4 different variants of Directed Acyclic Graphs:
- IOTA,
- Byteball,
- Hashgraph,
- NANO,
What is IOTA?
IOTA is a revolutionary variant of Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) technology, using a data structure called Tangle to provide low cost, rapid micro-transactions. Initially developed with the Internet-of-Things (IOT) in mind, the Tangle is a string of individual transactions that are interlinked, allowing for the transfer of value with no fees. This opens up many possibilities for the future of transactions, and IOTA is leading the way in its development and adoption.
What is Byteball in blockchain?
Byteball is a blockchain-based system that has a data structure similar to IOTA but uses a different consensus mechanism. Instead of using a traditional Proof of Work (POW) to validate transactions, Byteball uses an algorithm known as Main Chain. This algorithm is designed to confirm transactions using a series of steps that involve the whole network. It is a secure and reliable platform that can be used for a variety of applications, from financial services to data storage. Byteball is also known for its low transaction fees and fast transaction speeds.
What is Hashgraph in blockchain?
Hashgraph is a consensus algorithm that is used in distributed ledger technology, or blockchain. It is a consensus algorithm that is more efficient than traditional blockchain consensus algorithms, and uses a combination of directed acyclic graph (DAG) data structure and virtual voting to reach consensus. Hashgraph is faster and more secure than traditional blockchain consensus algorithms and provides better scalability. It is an exciting new technology that has the potential to revolutionize the blockchain industry.
What is NANO in blockchain?
Nano is a cryptocurrency based on the blockchain technology, designed to make digital payments fast, free and secure. It is a low-latency payment platform designed to make it easy for users to send, receive, and store funds with minimal fees. Nano is a decentralized cryptocurrency that uses a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) to store data which allows for quick and secure transactions. It uses a novel consensus algorithm which allows each account to be securely updated and maintained independently of the main blockchain. This allows for fast and secure transactions to be made with minimal fees and no need for miners or other third parties. With its efficient architecture, Nano is an ideal choice for merchants, traders, and users alike.
